Hyundai’s Robotic Microfactory Revolutionizes Car Production
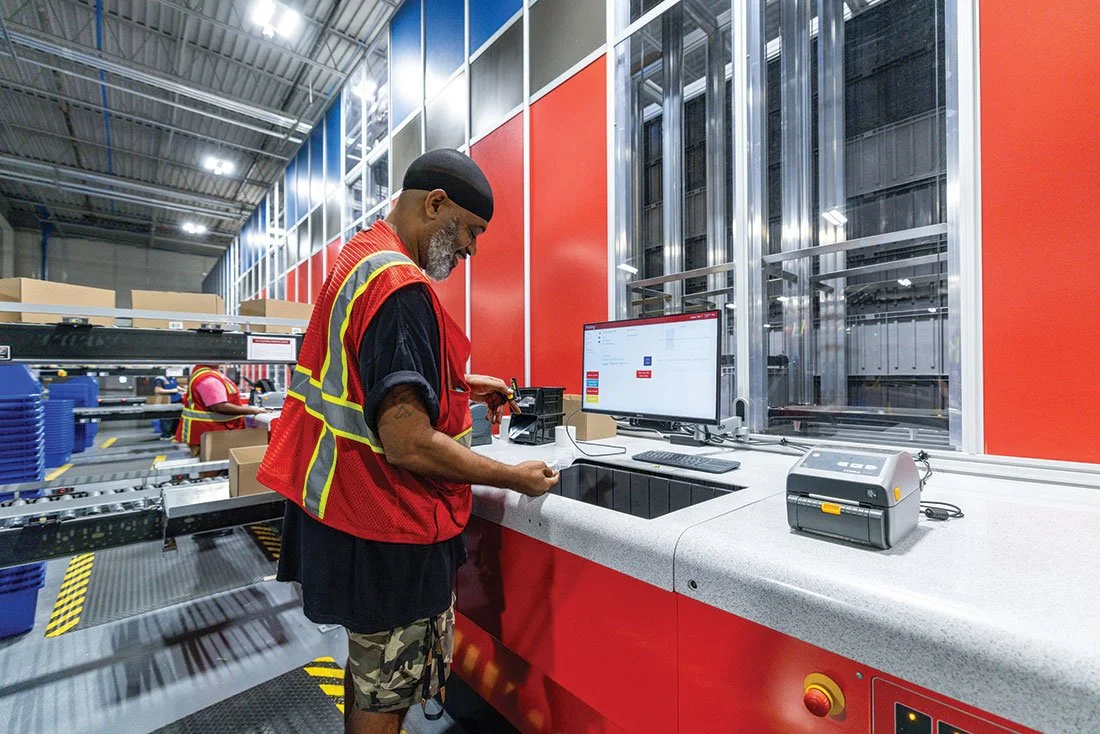
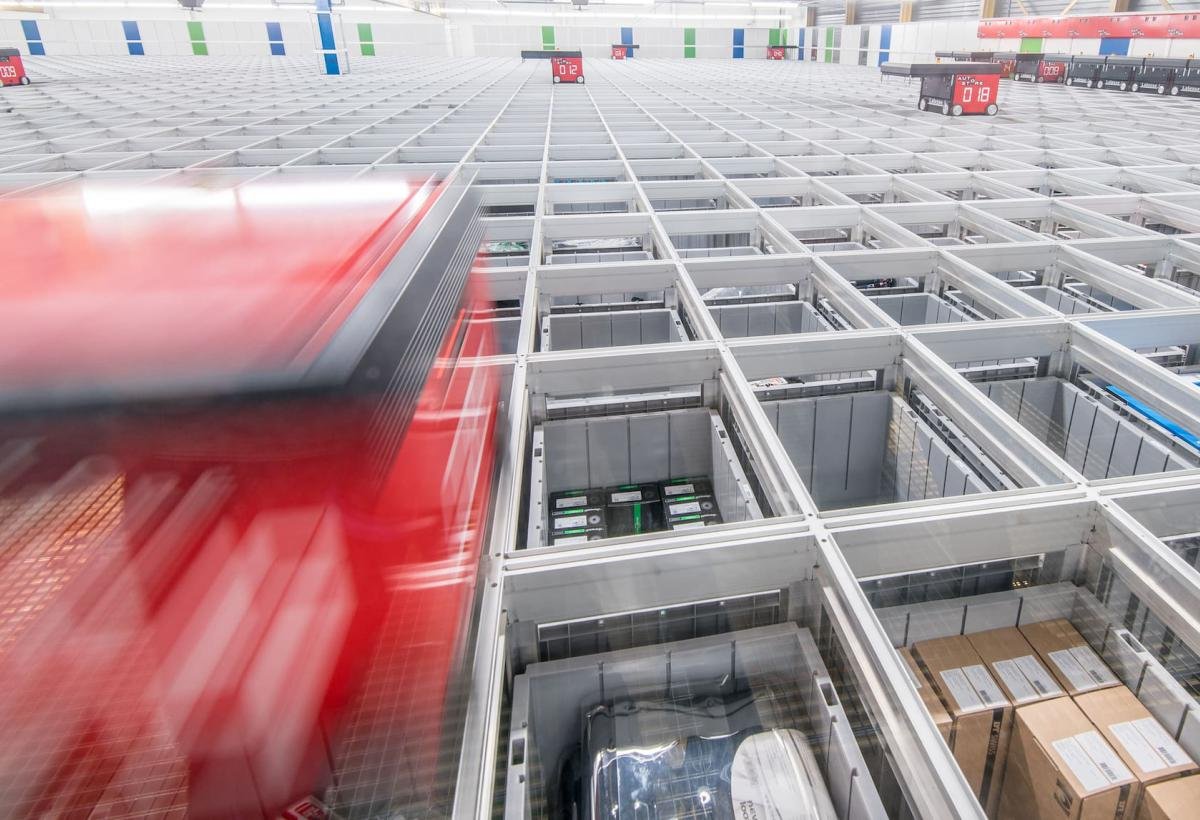
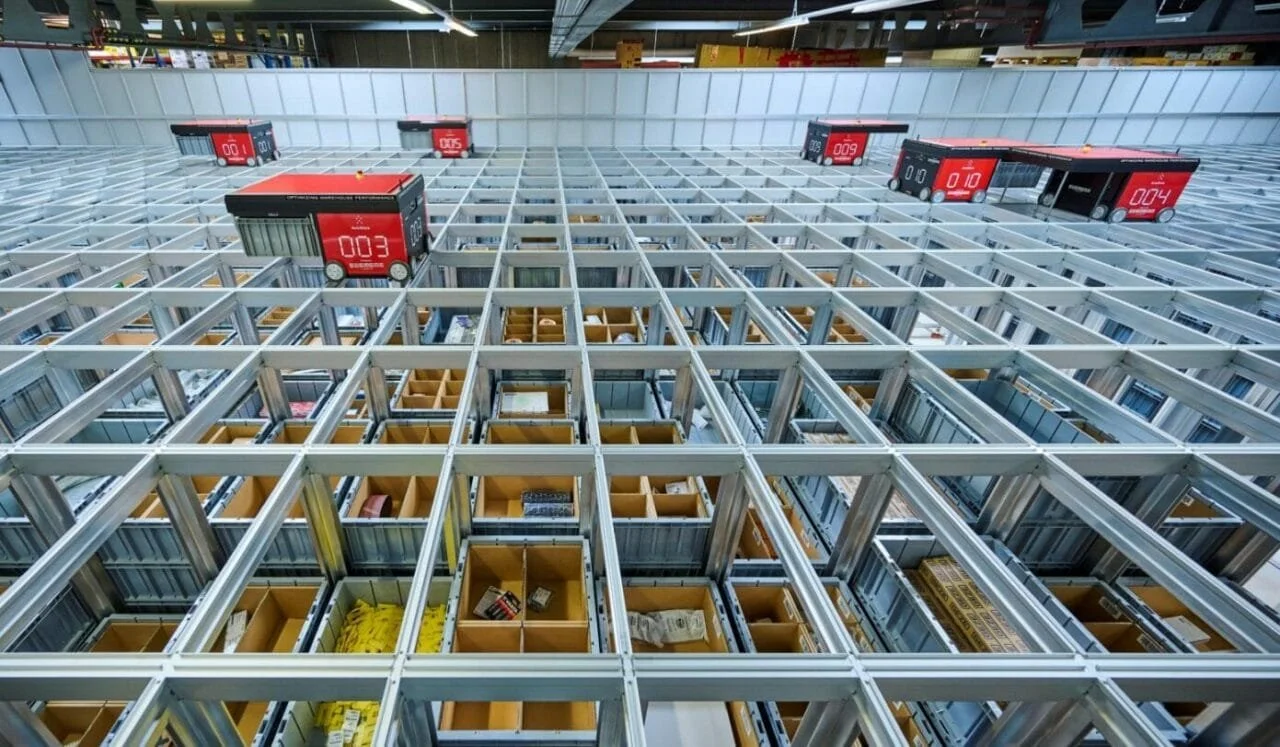
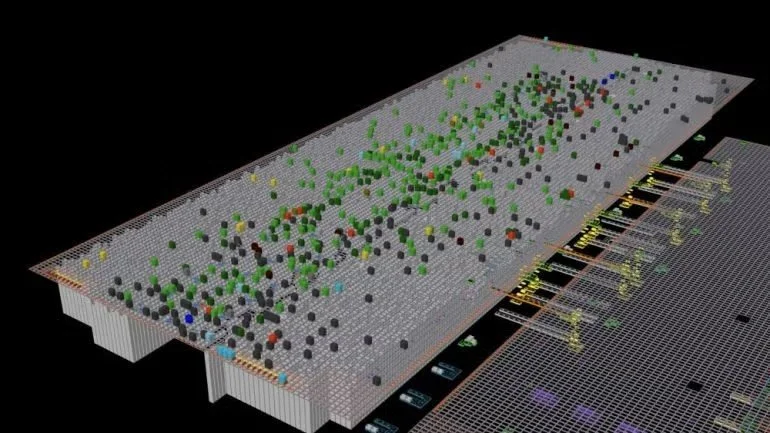
Hyundai’s cutting-edge microfactory in Singapore signals a leap into the future of automobile manufacturing. The facility employs a high level of automation with robots handling 60% of the production tasks, leading to a surprisingly small human workforce in the plant. The innovative cell-based production model differs from the traditional assembly line, providing adaptability and efficiency within a compact space.
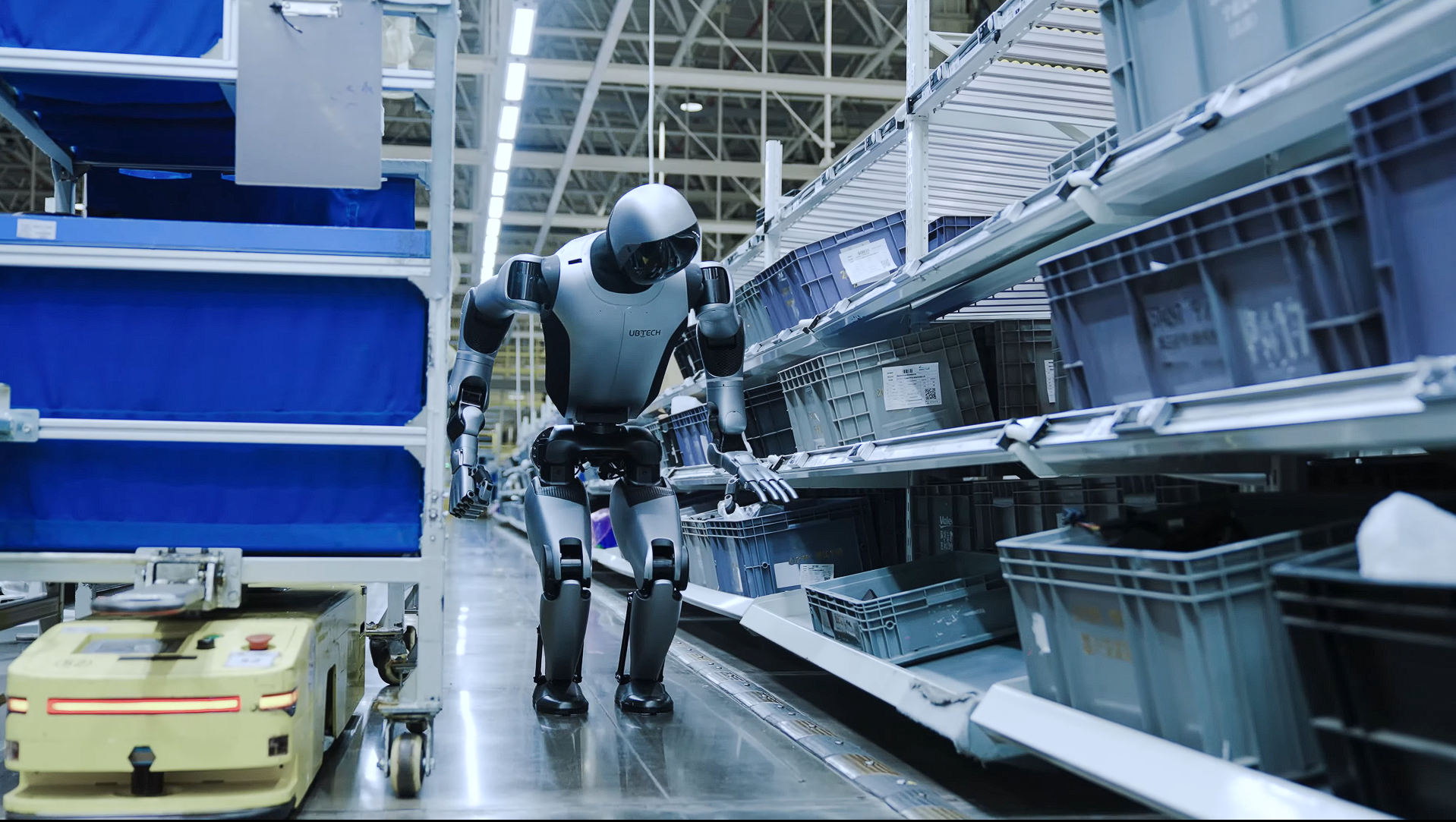
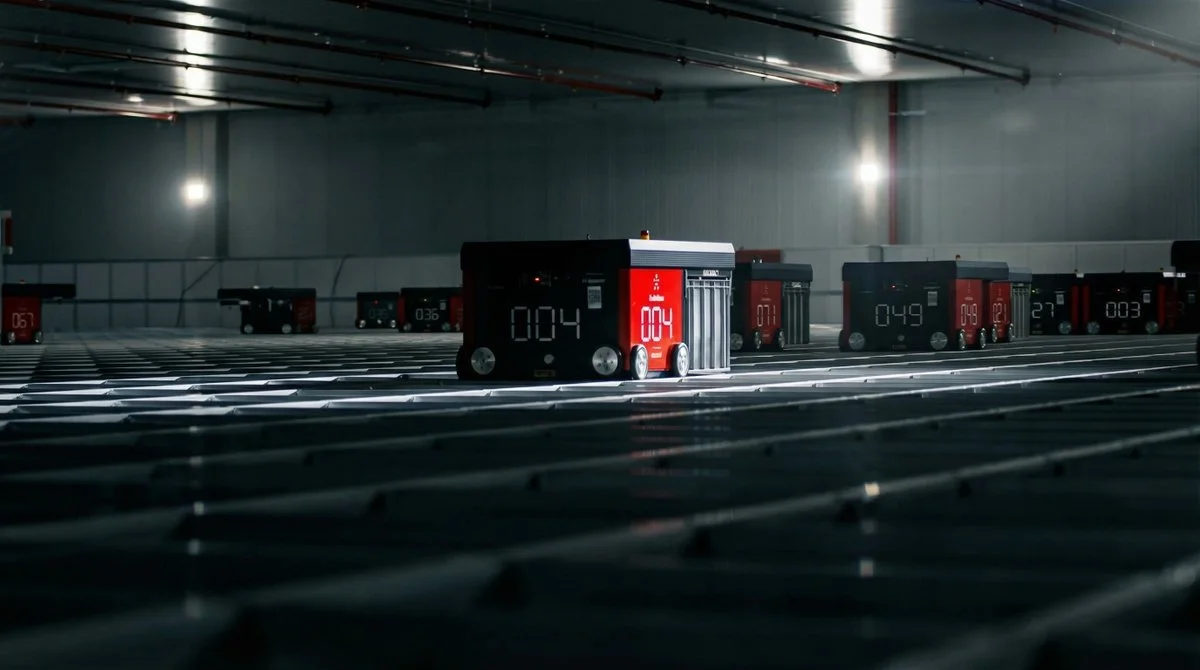
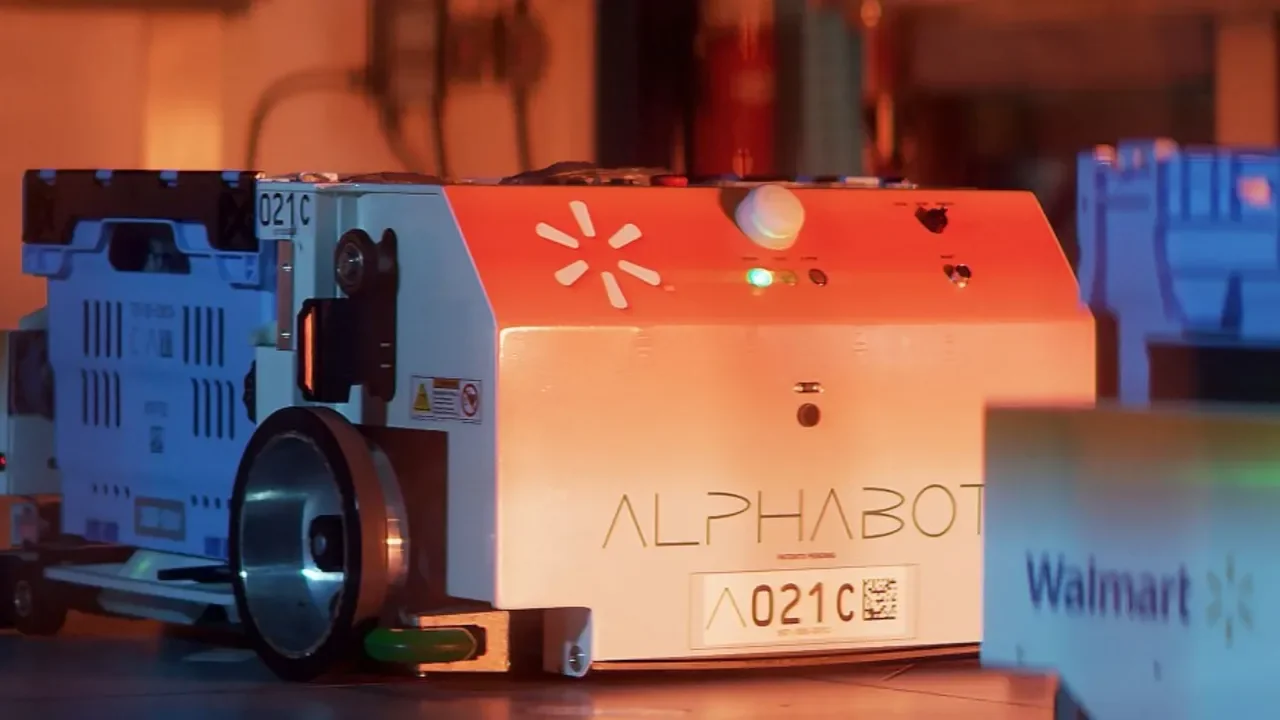
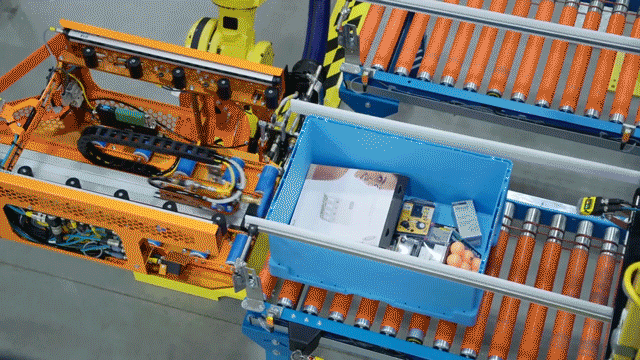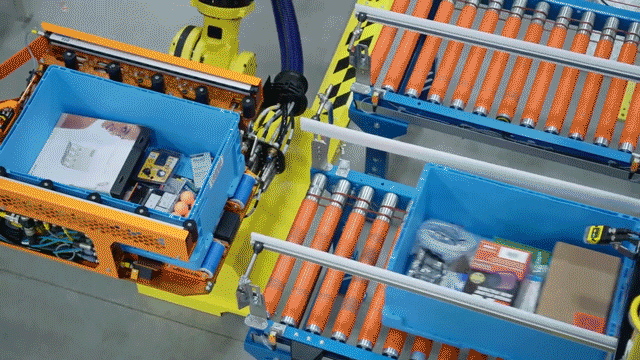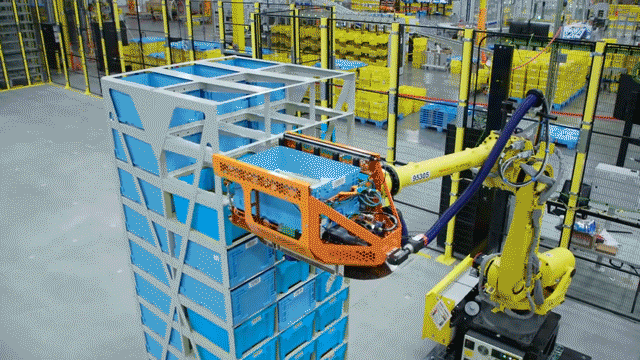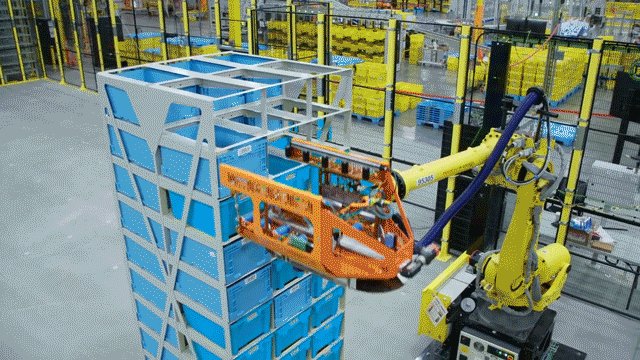
In a remarkable showcase of technology, Hyundai’s electric vehicle plant in Singapore looks like a vision brought to life from a utopian future. The advanced robotics in action include a robot dog named Spot from Boston Dynamics, which patrols the plant performing quality inspections. The plant also boasts autonomous robotic arms and self-driving ground vehicles that transport parts and electric vehicles throughout the facility.
The remarkable efficiency and automation in this microfactory mean that only 100 employees are needed to manufacture 30,000 vehicles annually. This approach to car production, using a cell-based system rather than the conventional production line, endows the microfactory with unparalleled flexibility in manufacturing. Each cell in the production process is equipped to adapt to different car models or variants without requiring significant restructuring.
Hyundai’s Singapore plant starkly contrasts with larger car factories, like Tesla’s Gigafactory in Texas, in both size and production methods. Despite being a fraction of the size of conventional factories, this microfactory represents an innovative solution for urban manufacturing where space is at a premium.
The future of this manufacturing style remains uncertain, particularly in regions where the workforce fears job displacement due to increased automation. Regardless, Hyundai’s venture into microfactory production is an important development to monitor as the industry trends toward more automated and efficient manufacturing processes.
FAQs About Hyundai’s Microfactory in Singapore
What is Hyundai’s microfactory in Singapore?
Hyundai’s microfactory in Singapore is a compact and highly automated facility that specializes in electric vehicle production. It utilizes advanced robotics and a cell-based production system to produce cars efficiently in an urban setting.
How does the microfactory’s production method differ from traditional car manufacturing?
Unlike the traditional assembly line approach, the microfactory uses a cell-based production model. Each cell is capable of adapting to various car models or variants, allowing for greater flexibility and efficiency without significant restructuring.
What role do robots play in Hyundai’s microfactory?
Robots are responsible for 60% of the production tasks within the microfactory. They include autonomous robotic arms, self-driving ground vehicles for transportation, and a robot dog named Spot from Boston Dynamics that performs quality inspections.
How many employees work at the microfactory, and what is its production capacity?
The microfactory operates with around 100 employees and has the capacity to manufacture 30,000 vehicles per year.
How does the size and efficiency of Hyundai’s microfactory compare to larger car factories?
Hyundai’s microfactory is significantly smaller than larger car factories such as Tesla’s Gigafactory. Despite its smaller size, it represents a solution for urban manufacturing and is just as efficient due to its innovative production methods.
What is the significance of the microfactory’s cell-based production model?
The cell-based production model is significant because it provides unparalleled flexibility within the manufacturing process. It can quickly adjust to produce different car models or variants without the need for major changes in the setup, which is ideal for a compact urban space.
What are the concerns surrounding the future of microfactory manufacturing?
One of the main concerns is the potential for job displacement due to the high level of automation in such plants. Workers fear that increased automation could lead to fewer manufacturing jobs.
Key Terms and Definitions:
– Microfactory: A small-scale factory with a high level of automation and adaptability, designed to operate efficiently in limited spaces.
– Cell-Based Production: A manufacturing system where different cells are each capable of handling various tasks and can be reconfigured for different products.
– Automation: The use of technology and machinery to perform tasks with minimal human intervention.
– Robotics: The branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots.